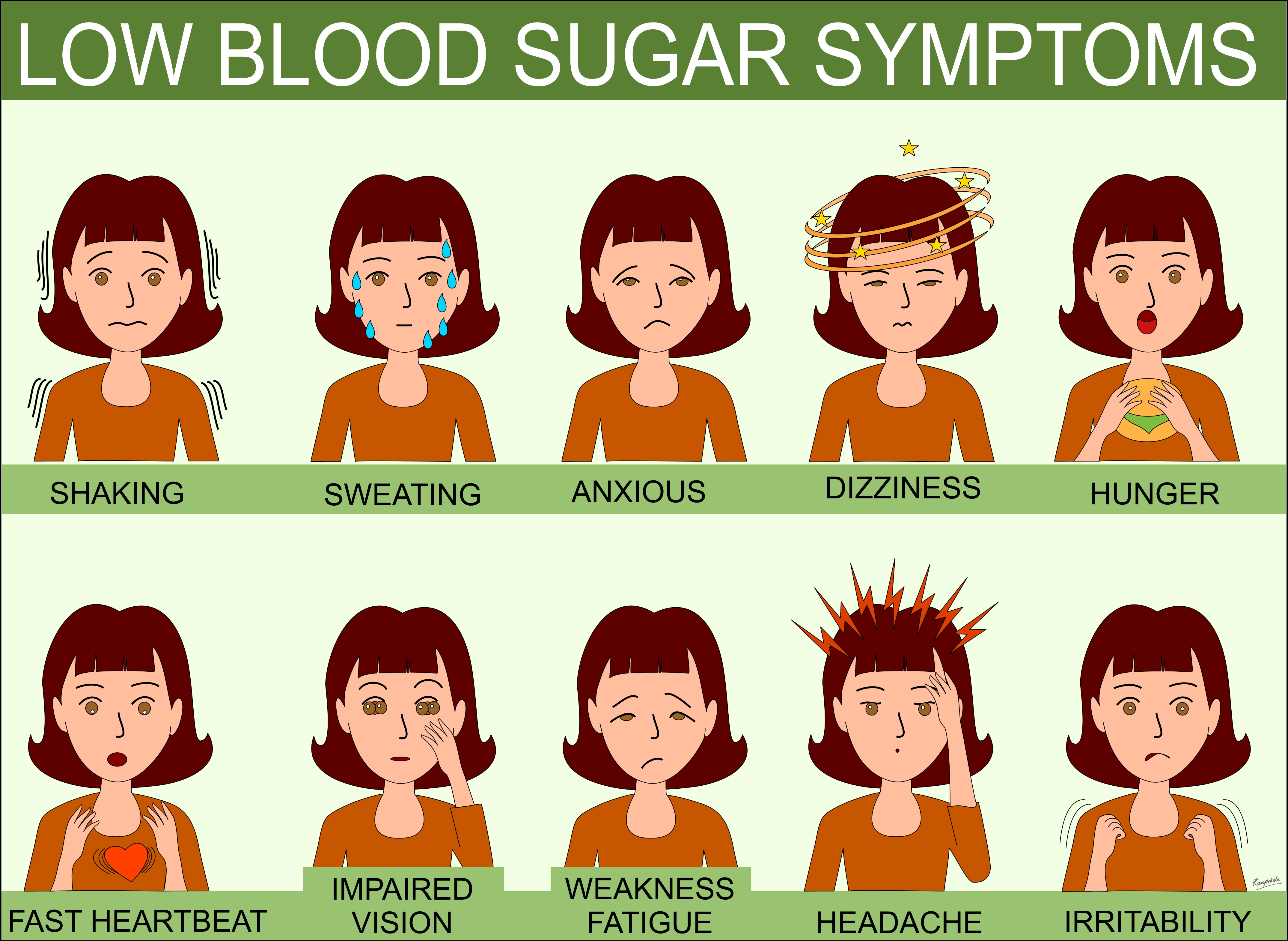
About Insulin
Insulin is the ONLY effective treatment for Type 1 Diabetes and it can be taken only as injections.

Different methods of injection:
Needles and syringes
Pen injections
Automatic injectors
Indwelling catheters
Insulin pumps
How to store Insulin? 
- AWAY from heat and direct sunlight
- NEVER let it freeze
- Keep unused bottles, cartridges and pens in the DOOR of the refrigerator
- Keep currently using bottles, cartridges and pens at the ROOM TEMPERATURE
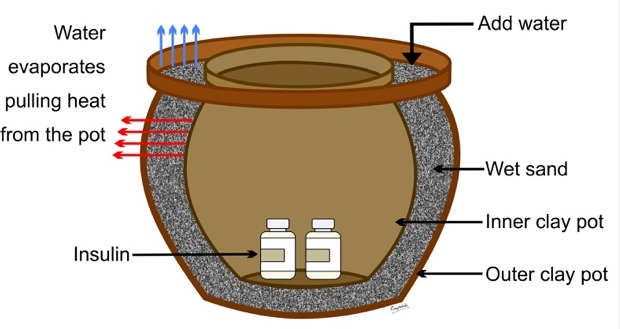
- If fridge is not available or there are frequent power cuts: store in an earthen pitcher kept in another EARTHEN BOWL filled with wet sand
TIPS FOR TRAVELLING WITH A CHILD WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES

COMPLICATIONS